The word “discount” refers to future value being discounted back to present value. The profitability index is the ratio of the present value of cash inflows to the present value of cash outflows. A profitability index greater than one indicates a profitable investment or project. Investors use NPV to evaluate potential investment opportunities, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, to determine which investments are likely to generate the highest returns.
Investment Analysis
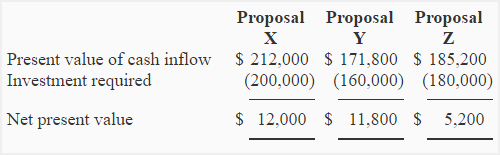
You expect to earn $10,000; $15,000; and $18,000 in 1, 2, and 3 years’ times respectively. We have a separate post on what capital budgeting is if you’re interested in learning more. But one of the most popular investment appraisal tools is the Net Present Value (NPV). Proposal X has the highest net present value but is not the most desirable investment. The present value indexes show proposal Y as the most desirable investment because it promises to generate 1.07 present value for each dollar invested, which is the highest among three alternatives.
Present Value Formula
By comparing NPVs, decision-makers can identify the most attractive investment opportunities and allocate resources accordingly. The primary capital budgeting techniques are the payback period method and the net present value method. If you haven’t quite understood it just yet, then please pause for a moment now. Take your time to think about the equation and think about how it is actually a function of two things — future expectations and risk. That’s how we incorporate the risk of not earning future expectations, into our estimate for the present value. And because this particular cash flow represents the cash in the present, we can essentially see this as the present value.
Example 4 – choosing among several alternative projects
On this page, first we would explain what is net present value and then look into how it is used to analyze investment projects in capital budgeting decisions. If we assume a discount rate of 6.5%, the discounted FCFs can be calculated using the “PV” Excel function. Thus, the $10,000 cash flow in two tax benefits for having dependents years is worth $7,972 on the present date, with the downward adjustment attributable to the time value of money (TVM) concept. The core premise of the present value theory is based on the time value of money (TVM), which states that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar received in the future.
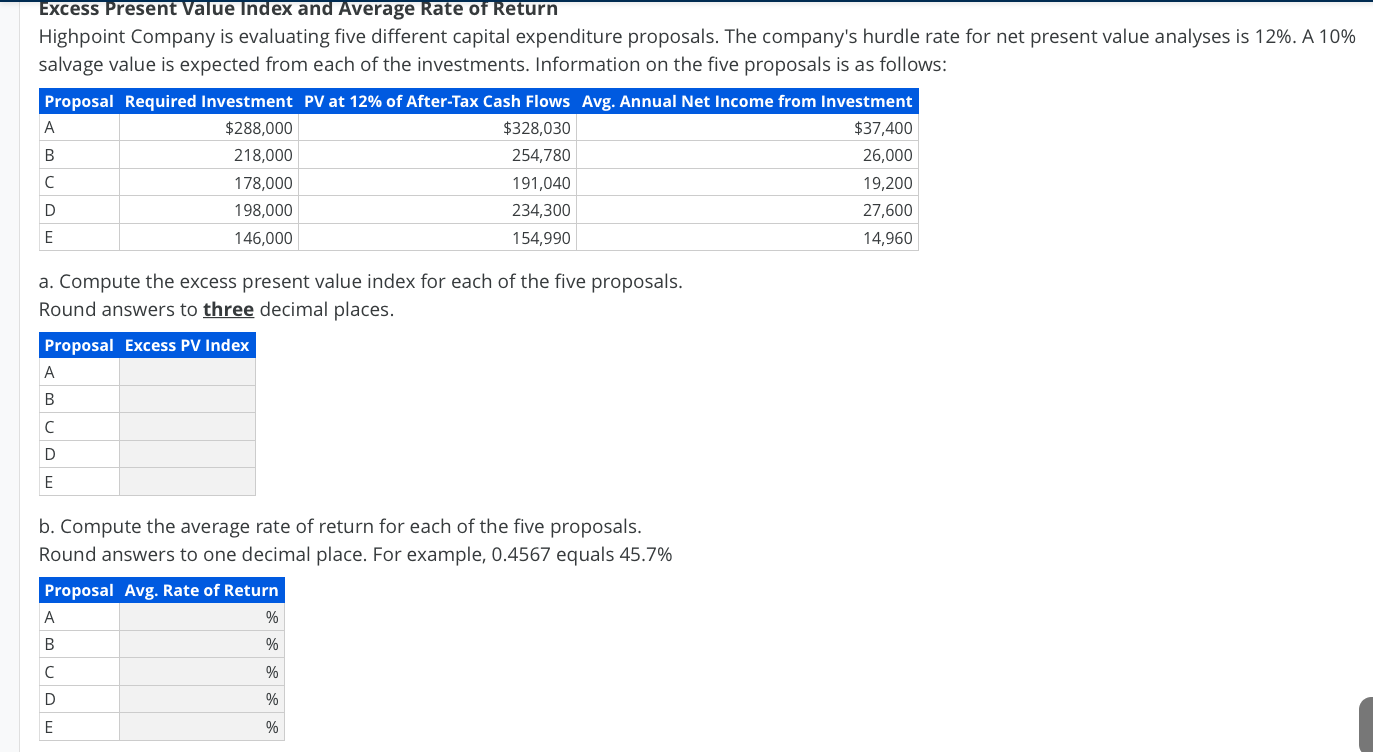
Once in place, the present value of these cash flows is ascertained and compared between each project. Typically, the project that offers the highest total net present value is selected, or prioritized, for investment. The cost of a project is $50,000 and it generates cash inflows of $20,000, $15,000, $25,000, and $10,000 over four years. The excess present value takes into account cash flows over time, as well as other economic variables, which provides more accuracy than simpler investment assessment tools. Additionally, the EPV allows for comparison of different investment options in terms of their present value.
NPV vs. PV Formula in Excel
- Companies frequently need to decide whether to allocate resources towards sustainable projects that could yield long-term benefits but might require substantial early-stage investments.
- Treasury bonds, which are considered virtually risk-free because they are backed by the U.S. government.
- Once in place, the present value of these cash flows is ascertained and compared between each project.
- Consequently, understanding and applying present value is deemed essential for anyone involved in investment decisions.
- While Present Value calculates the current value of a single future cash flow, Net Present Value (NPV) is used to evaluate the total value of a series of cash flows over time.
- Due to its complexity, there is a risk that the excess present value index will be misapplied or misunderstood by users who do not have sufficient financial acumen.
Much more on “discounting” further down, but we do also have a separate article on discounting future cash flows if you’re interested. The formula used to calculate the present value (PV) divides the future value of a future cash flow by one plus the discount rate raised to the number of periods, as shown below. In essence, the time value of money provides the mathematical backbone for present value computations, allowing us to translate future inflows and outflows into present values. The heart of this calculation lies in the idea that a dollar today provides more value, due to its earning potential, than a dollar in the future. This critical concept should underpin any financial decision you make, from personal investments to corporate finance, given its fundamental influence on the realm of economic and financial dynamics.
These cash flows include periodic coupon payments and the repayment of principal at maturity, all discounted back to the current day using a discount rate that reflects the riskiness of these cash flows. By comparing the present value of a bond’s cash flows with its market price, investors can determine if the bond is overpriced or underpriced, and thereby make informed investment decisions. The formula for calculating NPV involves taking the present value of future cash flows and subtracting the initial investment. The present value is calculated by discounting future cash flows using a discount rate that reflects the time value of money. Net present value is a financial calculation used to determine the present value of future cash flows.
Yes, the EPV allows for the comparison of different types of investments in terms of their present value. However, it is important to consider other factors such as risk levels when comparing different investment options before making a decision. Depending on how it is used, the excess present value index may provide inaccurate results if certain economic variables are not taken into account properly or other factors are ignored. Excess present value indexes are relatively easy to implement, making them ideal for business owners and other non-experts who need to make quick decisions about their finances.
Financial analysts and firms use the present value index to compare different projects. NPV is also applied in the valuation of securities, such as bonds, by calculating the present value of their future cash flows and comparing it to the current market price. By taking into account cash flows over a period of time, rather than just the initial investment, the EPV index can more accurately assess a company’s potential return on its investment. And take your time to see how we’re discounting future cash flows to get to the present value. It’s still fundamentally about “discounting” those future cash flows back to the present.
NPV is widely used in capital budgeting to evaluate the profitability of potential investments in long-term assets, such as machinery, equipment, and real estate. Finally, subtract the initial investment from the sum of the present values of all cash flows to determine the NPV of the investment or project. Using the discount rate, calculate the present value of each cash flow by dividing the cash flow by (1 + discount rate) raised to the power of the period in which the cash flow occurs. This calculation will provide the present value of each cash flow, adjusted for the time value of money.
The concept is that money received farther in the future is not as valuable as an equivalent amount received today. The further out we go in time, the more discounted the future value is, hence a lower present value. Represented by r in our formula, the interest rate is the cost or value tied to borrowing or lending money. It’s usually represented as a percentage of the principal amount on an annual basis.
Popularity: unranked [?]
