Gain or loss is computed by subtracting the asset’s net book value from the cash proceeds. Net book value is the asset’s original cost, less any related accumulated depreciation. Propensity Company sold land, which was carried on the balance sheet at a net book value of $10,000, representing the original purchase price of the land, in exchange for a cash payment of $14,800. The data set explained these net book value and cash proceeds facts for Propensity Company. The following section will show you how to prepare the statement of cash flows (indirect method for operating activities section) on page 259 from the financial statements on page 255. The net cash flows from operating activities adds this essential facet of information to the analysis, by illuminating whether the company’s operating cash sources were adequate to cover their operating cash uses.
- This year your company decided to sell the land and instead buy a building, resulting in the following transactions.
- Equipment with a cost of USD 20,000, on which USD 10,000 of depreciation had been recorded, was sold for USD 3,000 cash.
- On Propensity’s statement of cash flows, this amount is shown in the Cash Flows from Operating Activities section as an adjustment to reconcile net income to net cash flow from operating activities.
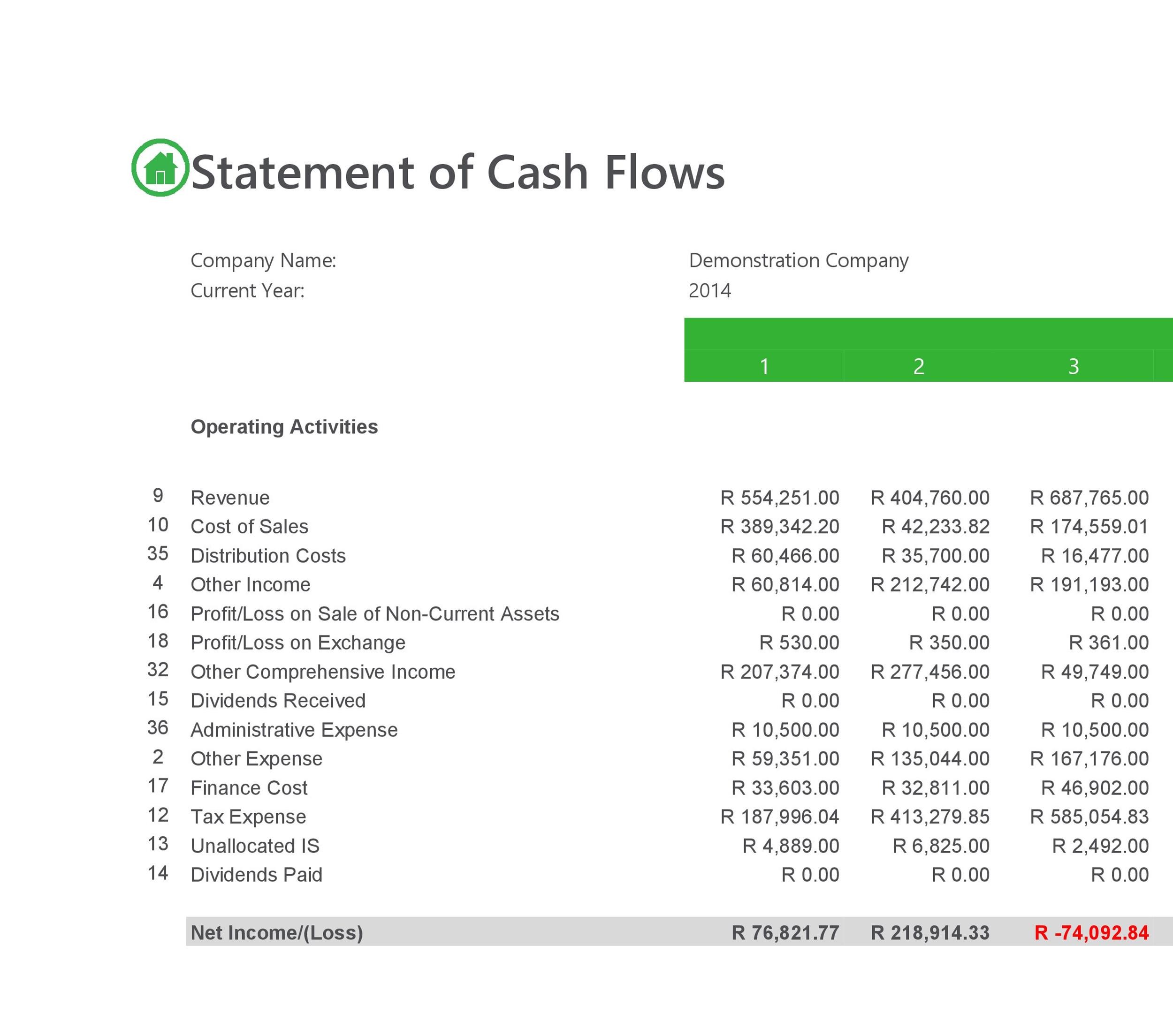
- The following is a sample statement of cash flows that has been prepared based on the financial statements presented on page 255.
- The following section will show you how to prepare the statement of cash flows (direct method for operating activities section) on page 270 from the financial statements on page 255.
4 Prepare the Completed Statement of Cash Flows Using the Indirect Method
My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. Receive the latest financial reporting and accounting updates with our newsletters and more delivered to your inbox. Operating activities pertain to the main operations of the business, such as purchasing and selling. Therefore, it does not evaluate the profitability of a company as it does not consider all costs or revenues. This information is helpful so that management can make decisions on where to cut costs. It also helps investors and creditors assess the financial health of the company.
Prepare the Operating Activities Section of the Statement of Cash Flows Using the Indirect Method
Thus, when a company issues a bond to the public, the company receives cash financing. In contrast, when interest is given to bondholders, the company decreases its cash. Cash-out transactions in CFF happen when dividends are paid, while cash-in transactions occur when the capital is raised. Transactions in CFF typically involve debt, equity, dividends, and stock repurchases.
Investing Activities Leading to an Increase in Cash
The cash flow statement is focused on the cash accounting method, which means that business transactions reflect in the financial statement when the cash flows into or out of the business or when actual payments are received or distributed. Assume that you are the chief financial officer of a company that provides accounting services to small businesses. Further assume that there were no investing or financing transactions, and no depreciation expense for 2018. Propensity Company had an increase in the current operating liability for salaries payable, in the amount of $400.
Example of the Statement of Cash Flows Indirect Method
Direct cash flow statements show the actual cash inflows and outflows from each operating, investing, and financing activity. While the indirect cash flow method makes adjustments on net income to account for accrual transactions. Increases in net cash flow from investing usually arise from the sale of long-term assets. The cash impact is the cash proceeds received from the transaction, which is not the same amount as the gain or loss that is reported on the income statement.
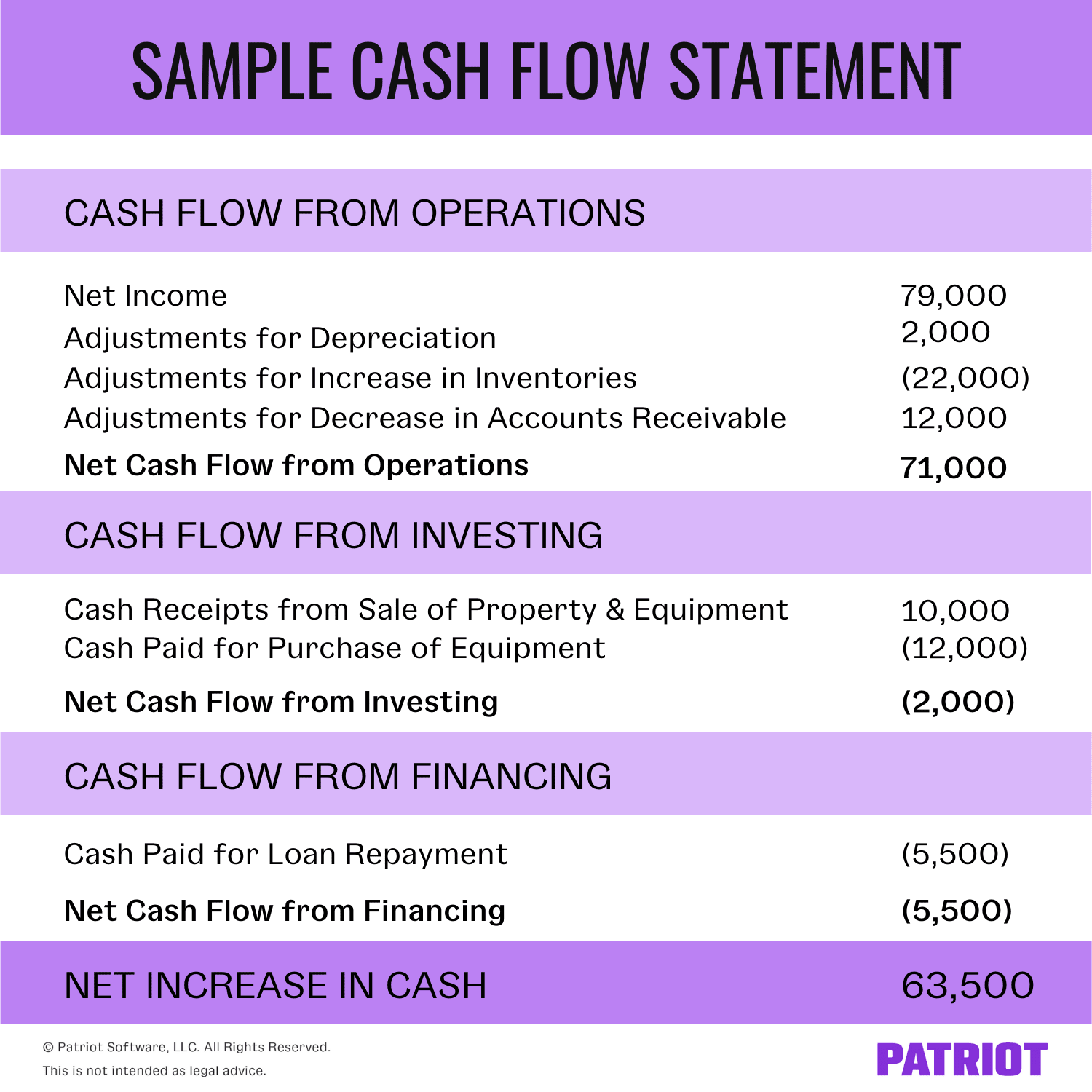
2.5 Comparative Operating Activities Sections – Statement of Cash Flows
Analysts look in this section to see if there are any changes in capital expenditures (CapEx). It can be considered as a cash version of the net income of a company since it starts with the net income or loss, then adds or subtracts from that amount to produce a net cash flow figure. Assume your specialty bakery makes gourmet cupcakes and has been operating out of rented facilities in the past. You owned a piece of land that you had planned to someday use to build a sales storefront. This year your company decided to sell the land and instead buy a building, resulting in the following transactions.
As a different possibility, an asset account such as Equipment may have experienced more than one transaction rather than just a single purchase. Using the same comparative balance sheet information as in the previous example, note that the information to its right in item d. There are relatively few items in the investing activities section, so it is reasonable to look at them one by one to determine if there is a cash inflow or outflow and, if so, its amount. us tax deadlines for expats businesses 2021 updated We explain cash flow classification issues and noncash disclosure requirements in detail, with special attention to recent SEC statements. We provide new and updated interpretive guidance on applying ASC 230 to many areas, including crypto assets, insurance contracts, debt securities, employee share purchase plans (ESPPs) and tax receivable agreements. Decreases in net cash flow from investing normally occur when long-term assets are purchased using cash.
Propensity Company had a decrease of $1,800 in the current operating liability for accounts payable. The fact that the payable decreased indicates that Propensity paid enough payments during the period to keep up with new charges, and also to pay down on amounts payable from previous periods. Therefore, the company had to have paid more in cash payments than the amounts shown as expense on the Income Statements, which means net cash flow from operating activities is lower than the related net income.
For decreases in prepaid assets, using up these assets shifts these costs that were recorded as assets over to current period expenses that then reduce net income for the period. Thus, cash from operating activities must be increased to reflect the fact that these expenses reduced net income on the income statement, but cash was not paid this period. Secondarily, decreases in accrued revenue accounts indicates that cash was collected in the current period but was recorded as revenue on a previous period’s income statement. In both scenarios, the net income reported on the income statement was lower than the actual net cash effect of the transactions. To reconcile net income to cash flow from operating activities, add decreases in current assets. The statement of cash flows prepared using the indirect method adjusts net income for the changes in balance sheet accounts to calculate the cash from operating activities.
Popularity: unranked [?]
